Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia And Dizziness
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/trigeminal-neuralgia-and-multiple-sclerosis-2440818_v2-012-b53eaece54614136a4b07402e640acd9.png)
There are two kinds of trigeminal neuralgia.
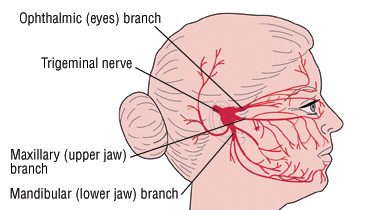
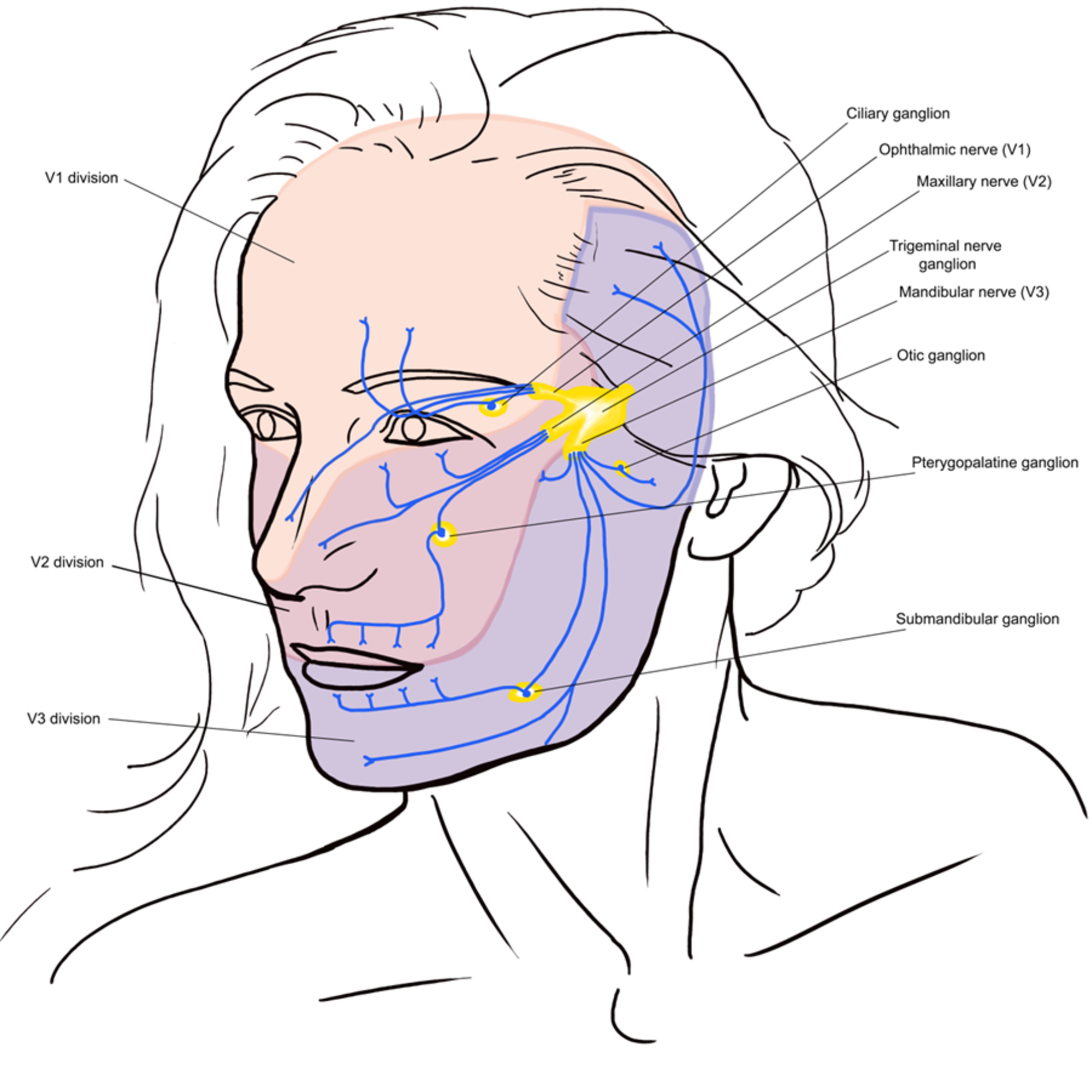
Atypical trigeminal neuralgia and dizziness. Patients with atypical trigeminal neuralgia experience episodes of sharp facial pain but they may also feel a dull constant ache as their baseline during normal functional activities. Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve which carries sensation from your face to your brain. The main symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is the sudden severe stabbing sharp shooting electric shock like pain on one side or both sides of the face. Atypical trigeminal neuralgia symptoms are more frequently burning and aching pain that is nearly constant and of somewhat lower intensity.
Typical trigeminal neuralgia and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. Trigeminal neuralgia is a nerve disorder that causes abrupt searing pain in the face and jaw. However the treatments for trigeminal neuralgia may cause dizziness. Trigeminal neuralgia most frequently affects people older than 50 and the condition is more common in women than men.
It is started at 150 mg per day and increased by 150 mg per week until pain relief is achieved. There are side effects such as dizziness and double vision but. This form of nerve pain is difficult to diagnose as it is rare and the symptoms overlap with several other disorders. Possible side effects include dizziness double vision drowsiness and nausea.
Atypical trigeminal neuralgia atn otherwise known as type 2 trigeminal neuralgia is a rare form of trigeminal neuralgia. Many authors use the diagnosis atypical tn. It is a disorder of the fifth cranial nerve trigeminal nerve where the nerve becomes inflamed and or demyelinates. When a patient shows no relief from this medication a physician has cause to doubt whether trigeminal neuralgia is present.
Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common cause of facial pain and is diagnosed in approximately 15 000 people per year in the united states. Trigeminal neuralgia pain is exceptionally severe. Its most common side effects include dizziness somnolence peripheral edema euphoria xerostomia dry mouth and weight gain. However the effectiveness of carbamazepine decreases over time.
Trigeminal neuralgia usually does not lead to dizziness. In the early stages of the disease carbamazepine controls pain for most people. It affects about one million people worldwide and is more common in women and people aged over 50. This is sometimes referred to as type 2 trigeminal neuralgia or tn2 with typical trigeminal neuralgia referred to as type 1 or tn1.
Around 4 5 people per 100 000 have trigeminal neuralgia and a small subset of those have atn. Check trigeminal neuralgia atypical on downloadsearch. Atypical trigeminal neuralgia is a type of trigeminal neuralgia that is identified by the constancy of symptoms.