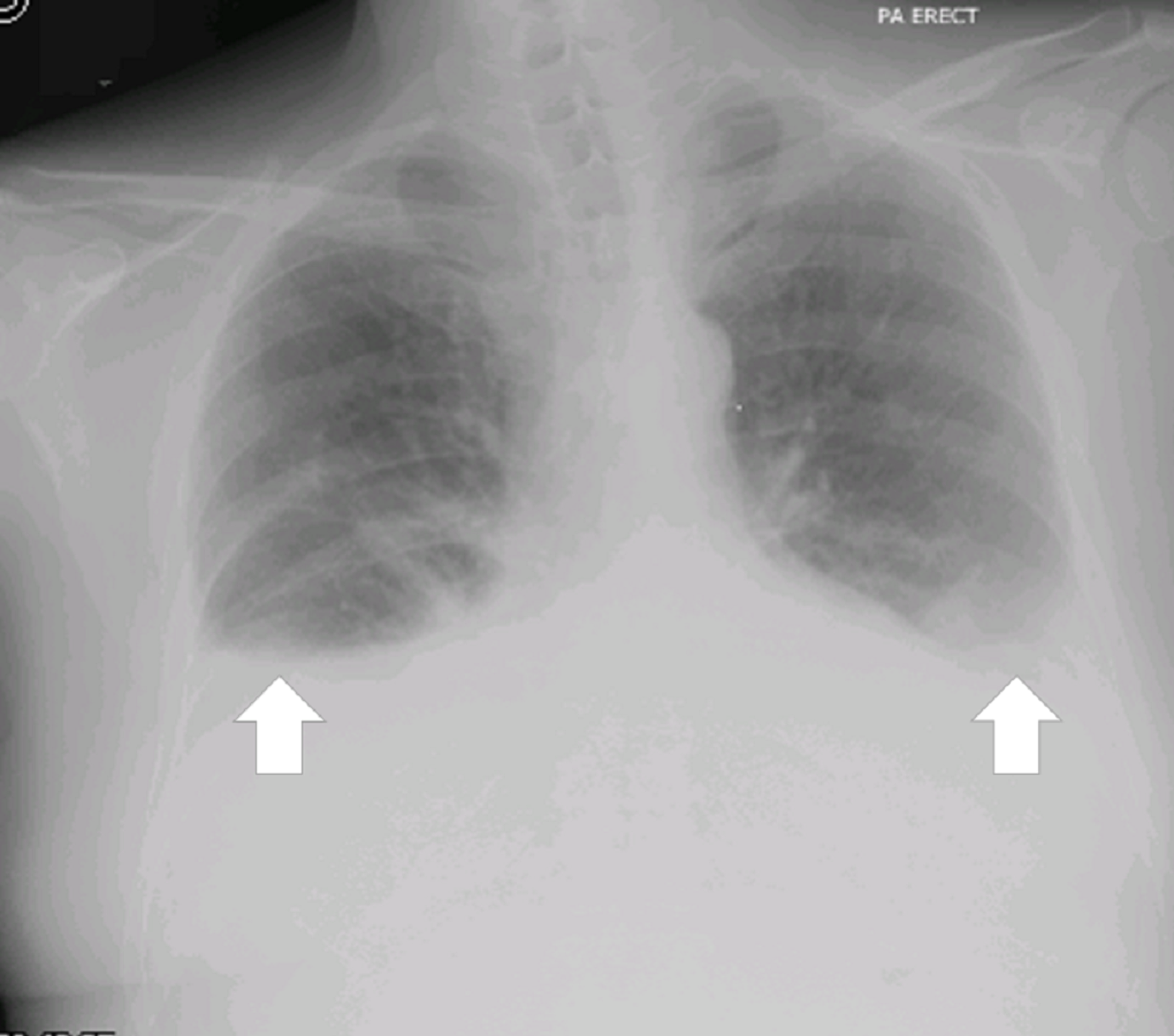
Bilateral Effusions Lungs

A pleural effusion is an unusual amount of fluid around the lung.
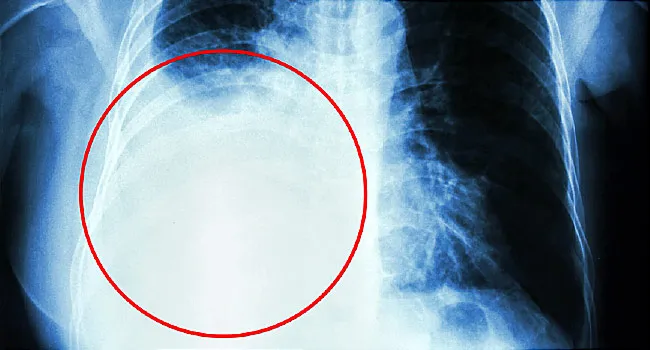
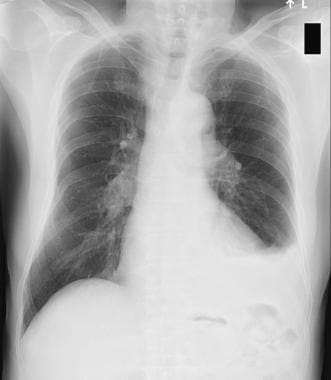
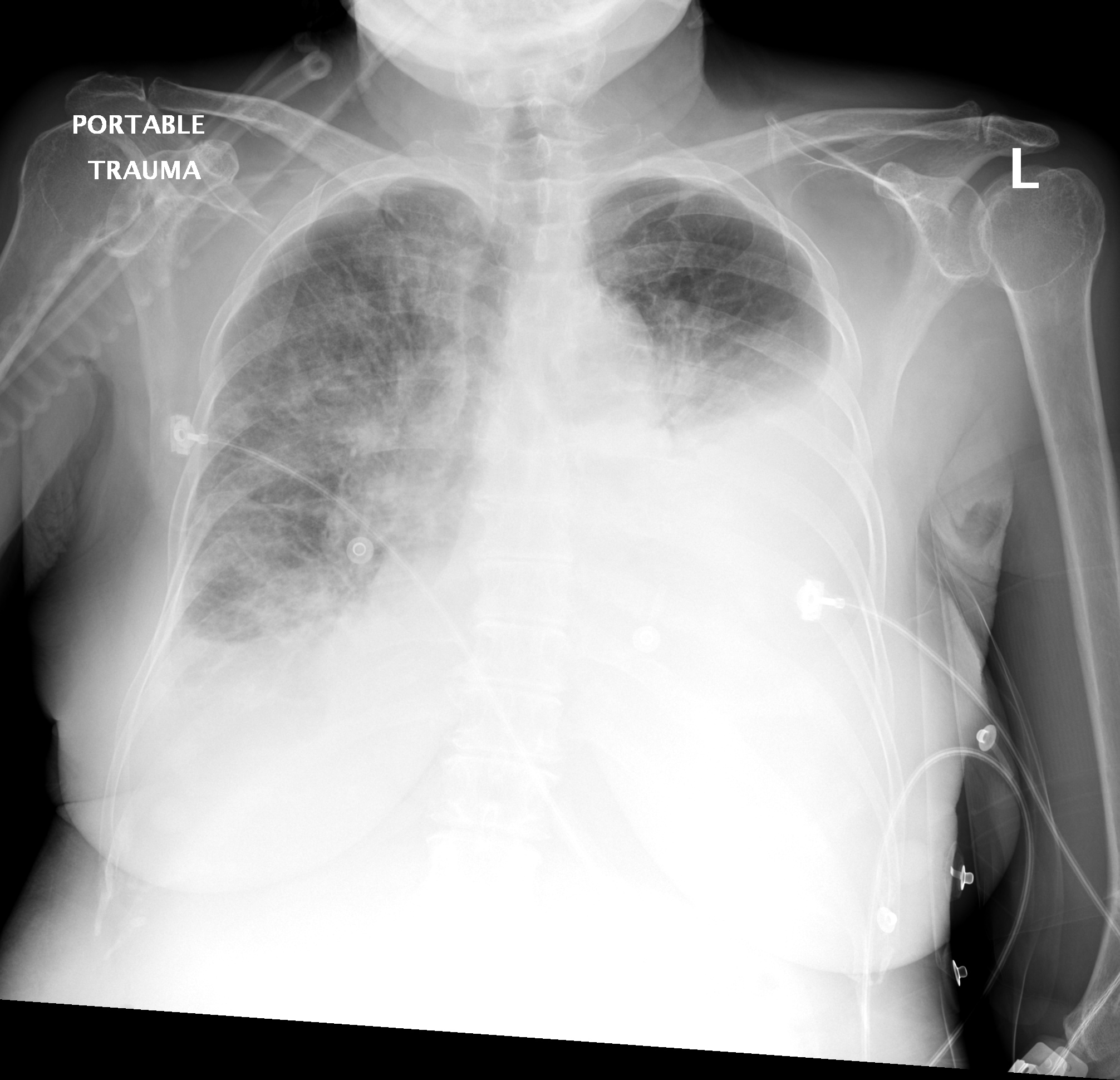
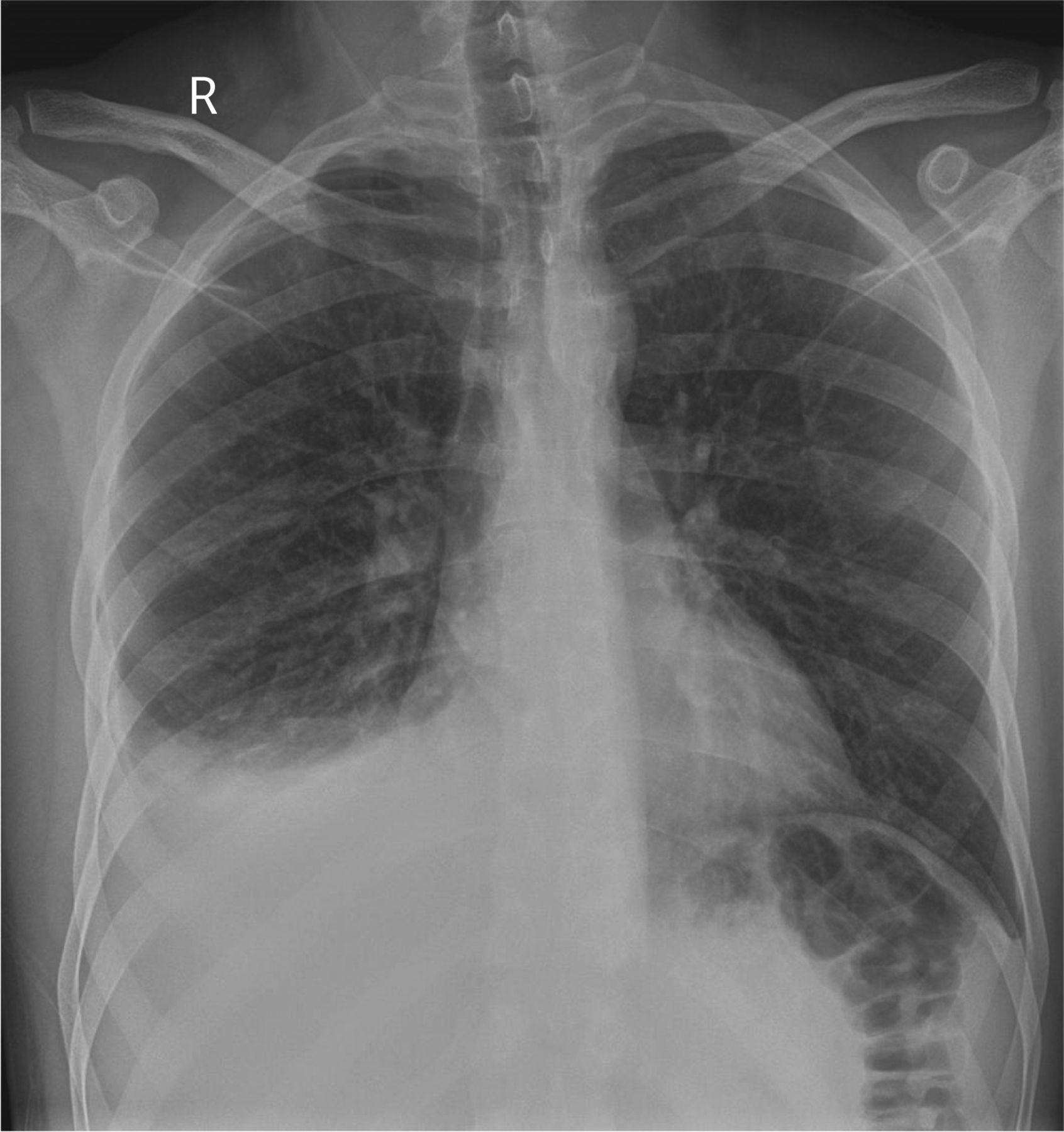
Bilateral effusions lungs. A small amount of fluid normally fills the pleural cavity and helps the lungs glide smoothly in the chest as we breathe. The center team will help care for you and your infant with a pleural effusion. Unfortunately it is difficult to predict the severity of the lung damage based on prenatal ultrasounds or even shortly after birth. A bilateral pleural effusion occurs when fluid between the lungs and chest dysfunctions creating fluid accumulation.
There s always a small amount of liquid within this lining to help lubricate the lungs as they. In some cases of pleurisy fluid builds up in the small space between the two layers of tissue. Pleurisy can be accompanied by pleural effusion atelectasis or empyema. It is also not uncommon for this type of effusion to occur in heart patients especially those who have recently had heart surgery.
The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity and act to lubricate and facilitate breathing. This is called pleural effusion. Normally a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura. Pleural effusion is buildup of fluid between the chest wall and the lung.
Most cases of pleural effusion are mild and children will grow up with normal lung function. Chest x ray can detect pleural effusions as they usually appear as whitish areas at the lung base and they may occur on only one side unilateral or on both sides bilateral. This complication can be the result of a pulmonary embolism or a preexisting cirrhosis condition. Pleural effusion sometimes referred to as water on the lungs is the build up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs.
When mesothelioma or another condition causes excess fluids to accumulate the result is a pleural effusion.