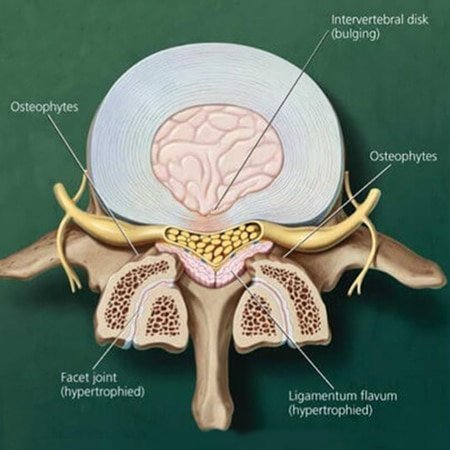
Bilateral Facet Arthropathy And Ligamentum Flavum Redundancy
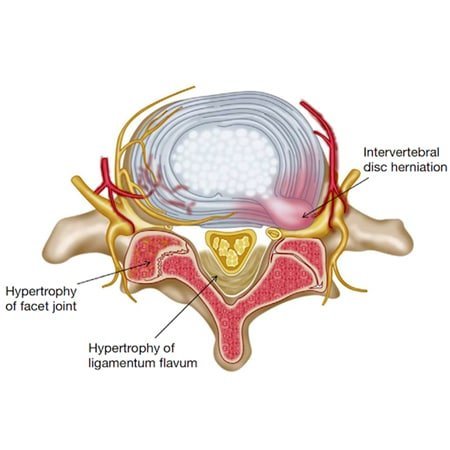
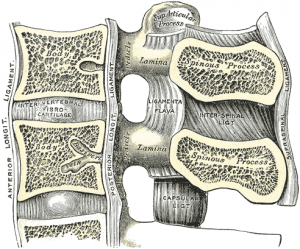
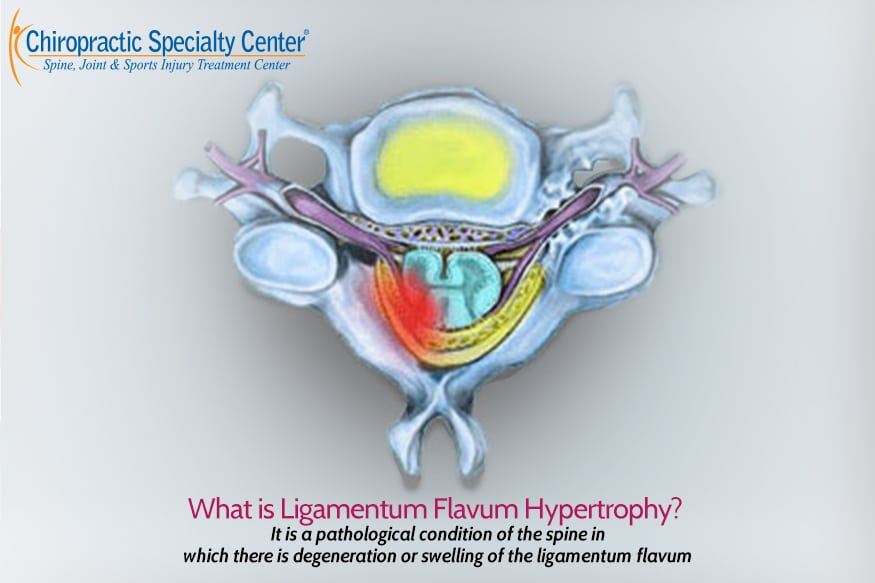
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy also known as ligamentum flavum thickening is a health condition related to the spine and lower back.
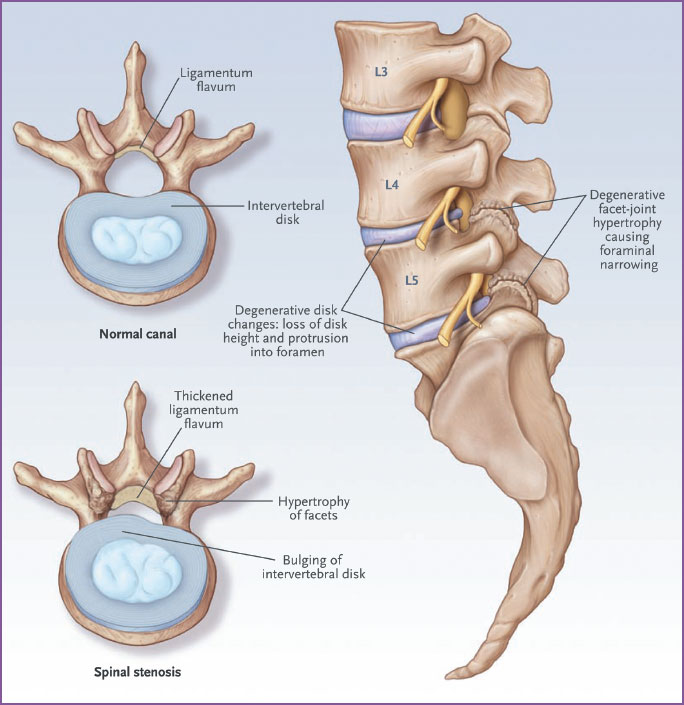
Bilateral facet arthropathy and ligamentum flavum redundancy. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy details. Axial mris demonstrate central and lateral recess stenosis with facet arthropathy. The pressure or load on your facet joints is reduced when you bend your body forward into a spinal flexion position. Since this is quite a complicated medical issue the purpose of this.
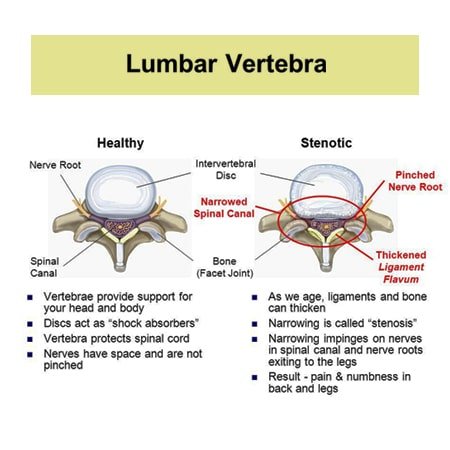
The best treatment for hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum. Mark weston answered 30 years experience orthopedic spine surgery. Facet arthropathy pain is typically relieved by bending forward. Is ligamentum flavum and facet hypertrophy the same as spinal stenosis.
What is a combination of concentric disc displacement facet arthropathy and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum result bilateral lateral recess stenosi dr. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum is a common finding in patients with a herniated disc protruded disc prolapsed disc or extruded disc slipped disc or slip disc injury poor posture and longstanding spine conditions are the leading cause of hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc prolapsed disc extruded disc or slipped disc or protruded disc. However when conditions are perfectly met ligamentum flavum thickening can create symptomatic and possibly extreme stenosis symptoms in some patients.
Sagittal mris reveal central stenosis with a synovial cyst at l4 l5. Animal study suggests stress on back causes hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum. The severe symptoms like back pain tingling numbness and muscle weakness are observed in patient. 2 such stress may cause hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in manual worker.
What is a combination of concentric disc displacement facet arthropathy and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum result bilateral lateral recess stenosi dr. Partial spinal stenosis is rarely anything of consequence and is actually a completely normal part of aging for the cervical and lumbar spinal regions. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy or ligamentum flavum thickening can also be caused due to normal wear and tear of the spinal cord with age. Limited spine films demonstrate facet arthropathy is greater at l5 with minimal degenerative subluxation.