Bilateral Hilar Lymphadenopathy Causes

Conditions such as sarcoidosis amyloidosis and silicosis can cause hilar lymphadenopathy.
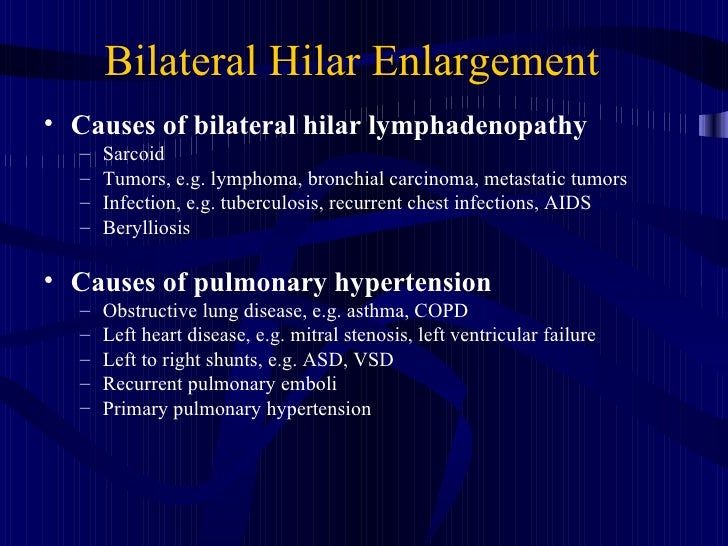
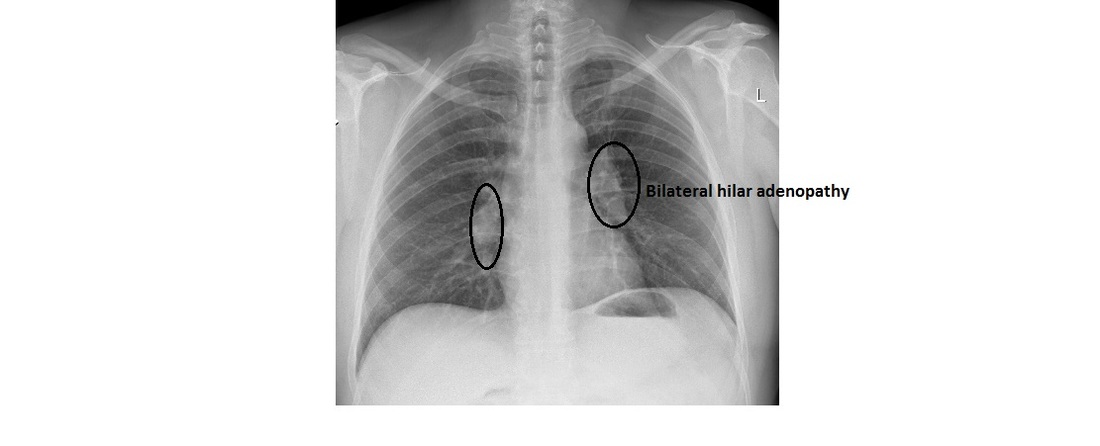
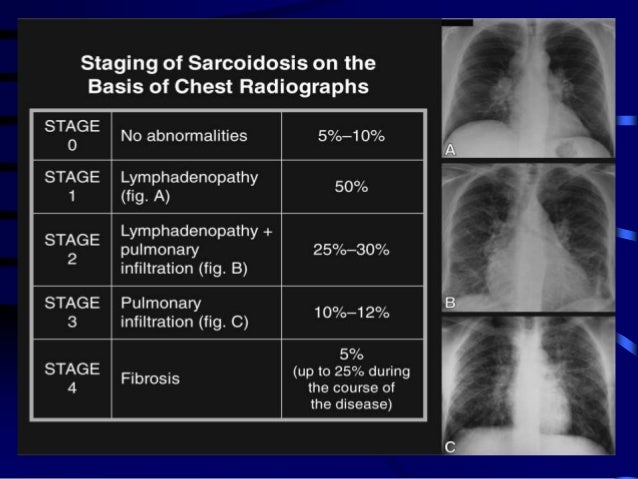
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy causes. Sarcoidosis is the most common cause of bilateral hilar lymph node enlargement especially in young adults. Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy is a bilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes of pulmonary hila. The following are causes of bhl. Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease that affects primarily the lung and lymphatic system.
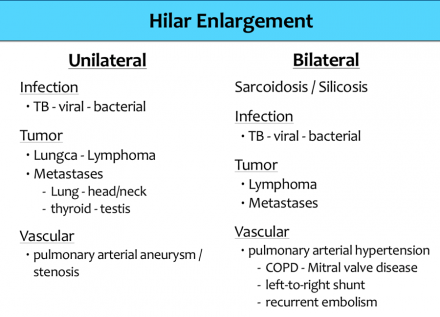
In younger patients with bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy sarcoidosis should be the diagnosis of exclusion because by a large margin it is the most common cause. Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy or bilateral hilar lymph node enlargement can arise from many causes which include 6. Primary tuberculosis fungal infection atypical mycobacterial infection viral infection tularemia anthrax bronchogenic carcinoma lymphoma sarcoidosis and silicosis. The four most common causes of radiographically detectable mediastinal lymphadenopathy are sarcoidosis lymphoma metastatic tumor and granulomatous infections.
The hilar lymph node enlargement with sarcoidosis is usually symmetric in contrast to other common causes. Metastatic or primary hilar tumor bronchogenic carcinoma lymphoma. Another common cause is a bacterial infection like strep throat. Lymphadenopathy can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection malignancy or an autoimmune disease the most common causes of swollen glands include.
Sarcoidosis silicosis drug reaction. More common in hodgkin lymphoma than non hodgkin lymphoma. The most common cause of swollen lymph nodes is a viral infection like the common cold or flu. More rarely lymph nodes can swell.
The following conditions lead to the appearance of unilateral or bilateral symmetrical hilar adenopathy. Bilateral hilar lymph node enlargement can arise from many causes which include.