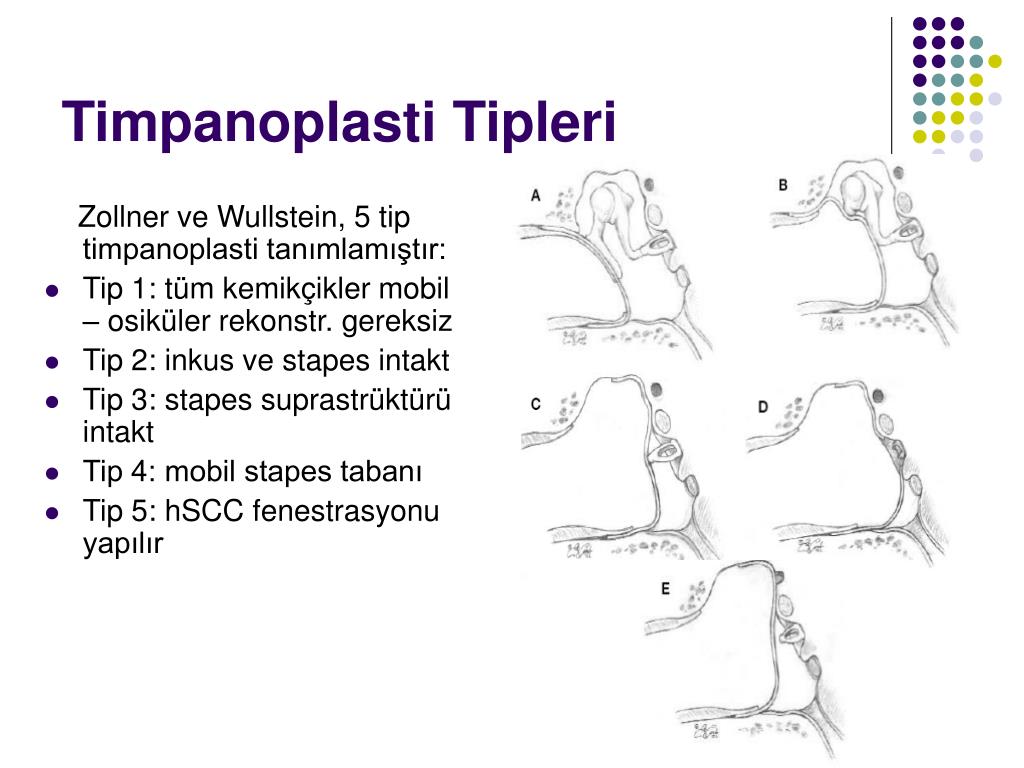
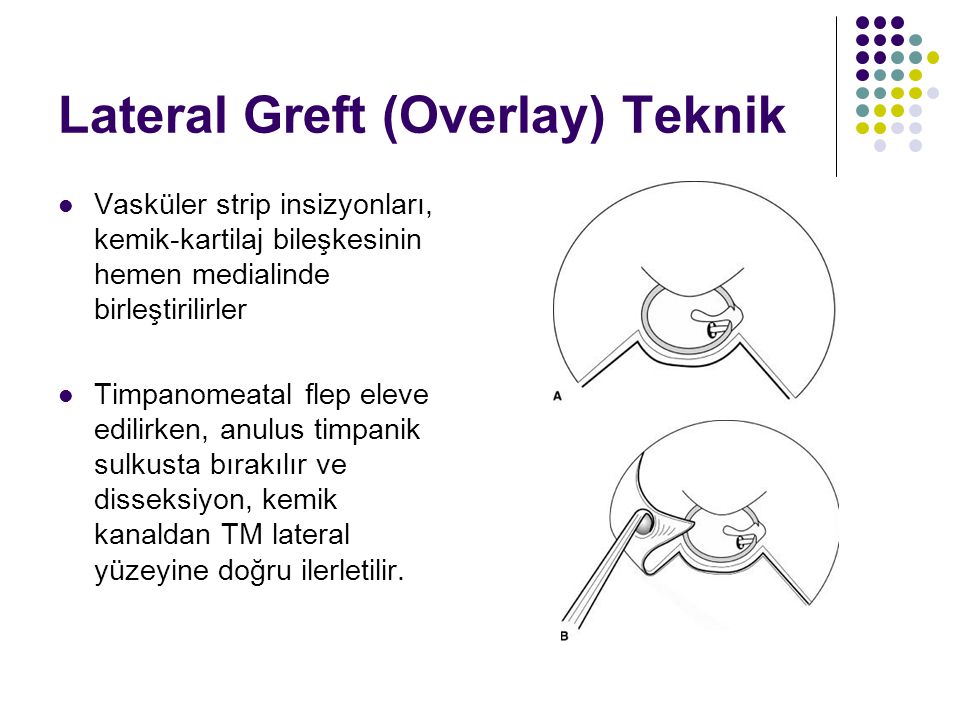
Bilateral Timpanik Membran Intakt Nedir
The tympanic membrane should appear as an intact ovoid semitransparent pearly gray membrane at the end of the canal.
Bilateral timpanik membran intakt nedir. Timpanik membran ne demek timpanik membran hakkında bilgi sağlık rehberi. Perforations can be temporary or persistent. A 72 year old male presented with acute. 4 5 patients.
Most tympanic membrane perforations tmps are diagnosed using routine otoscopy. The handle of the malleus should be seen near the center of the pars tensa. The tympanic membrane or eardrum is a thin membrane that separates the outer ear canal from the middle and inner ear. Tympanic membrane perforations tmps can result from disease particularly infection trauma or medical care.
The most common causes of hemotympanum are therapeutic nasal packing epistaxis blood disorders and blunt trauma to the head. Your eardrum also called the tympanic membrane is a thin layer of tissue that separates the outer part of your ear from your middle ear it sends sound vibrations from the world around you to. Gently straighten out the ear canal by pulling the external ear superiorly and posteriorly. 1 3 the presence of blood in the tympanic cavity can lead to conductive or mixed pattern of hearing loss.
A rare case of spontaneous bilateral hemotympanum in a patient treated with anticoagulants is presented herein. Hemotympanum is described as the presence of blood in the middle ear cavity in the setting of an intact tympanic membrane. The eardrum comprises two parts the pars tensa which is the main part of the eardrum and the pars flaccida which is a smaller part of the eardrum located above the pars tensa either or both of these parts may become retracted. Hold the otoscope like a pen between thumb and index finger left hand for left ear and right hand for right ear resting your little finger on the patient s cheek this acts as a pivot.
The upper fifth the pars flaccida. The lower four fifths of the tympanic membrane is called the pars tensa. Effect varies with size location on the drum surface and associated pathologic condition. Hemotympanum is characterized as idiopathic when it is detected in the presence of chronic otitis media.
The eustachian tubes are also located in the middle ear. Tympanic membrane retraction describes a condition in which a part of the eardrum lies deeper within the ear than its normal position. In hemotympanum the involved tympanic membrane may appear red or dark blue to near black in color depending on the age of the blood.