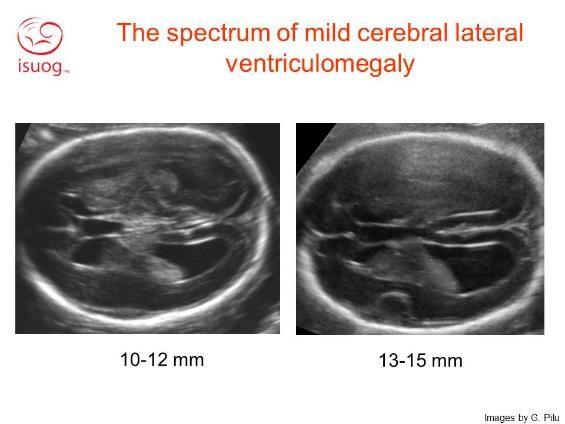
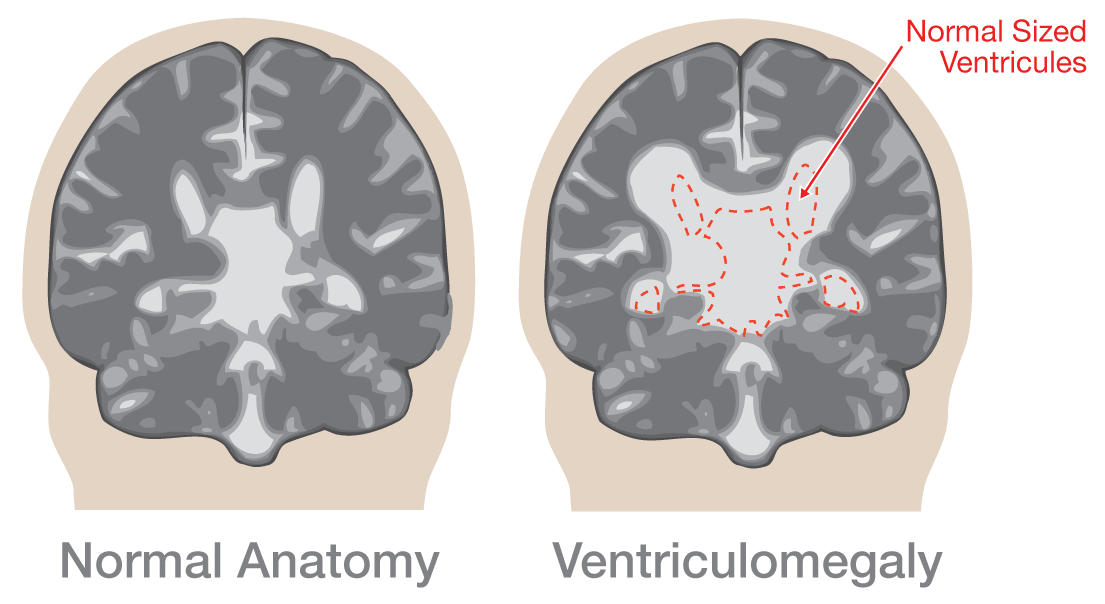
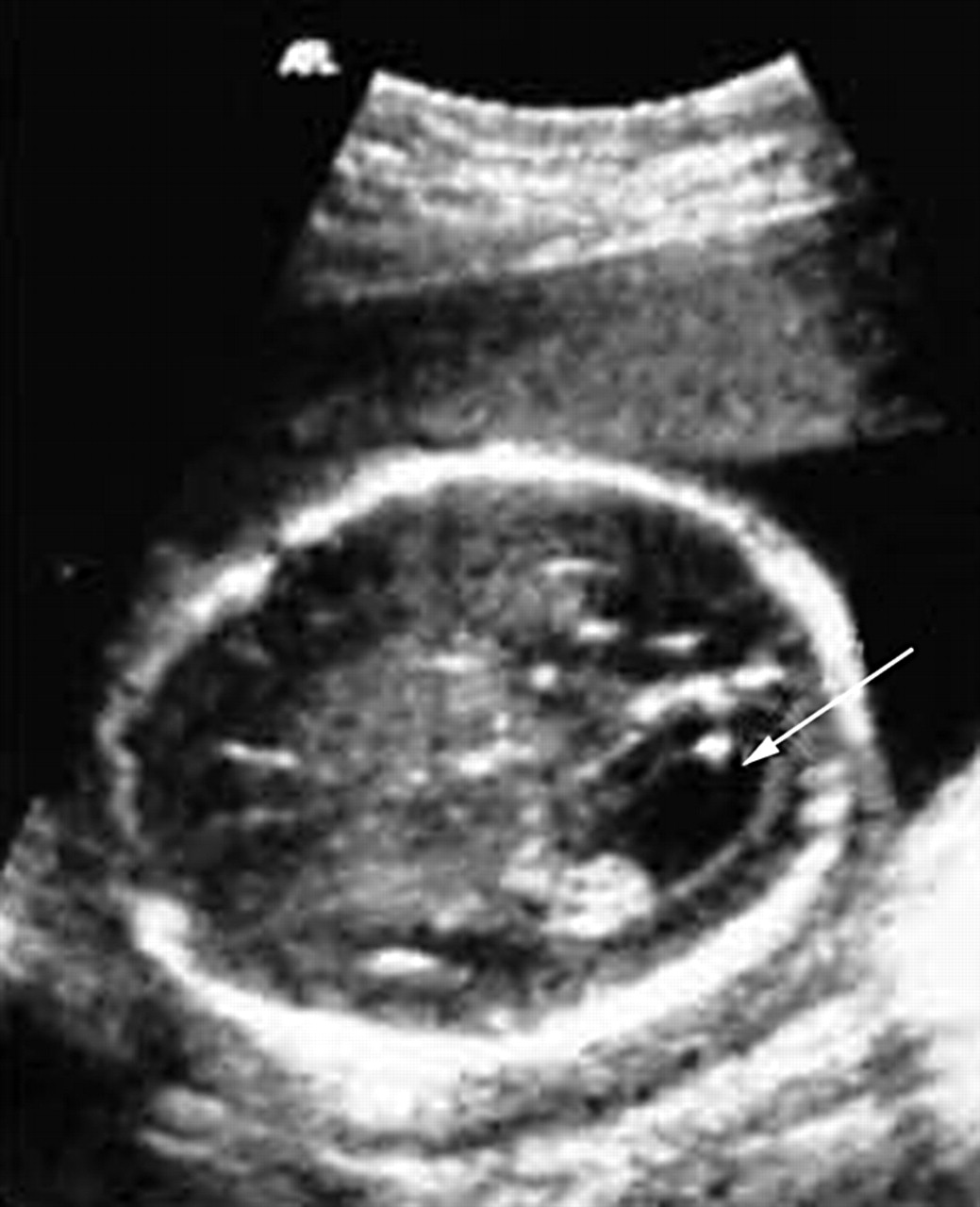
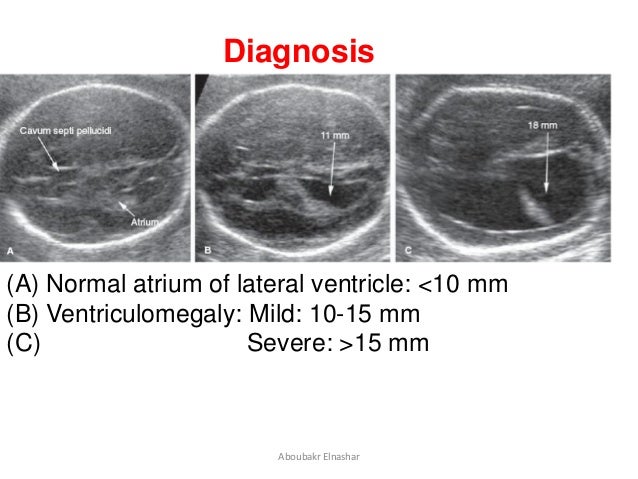
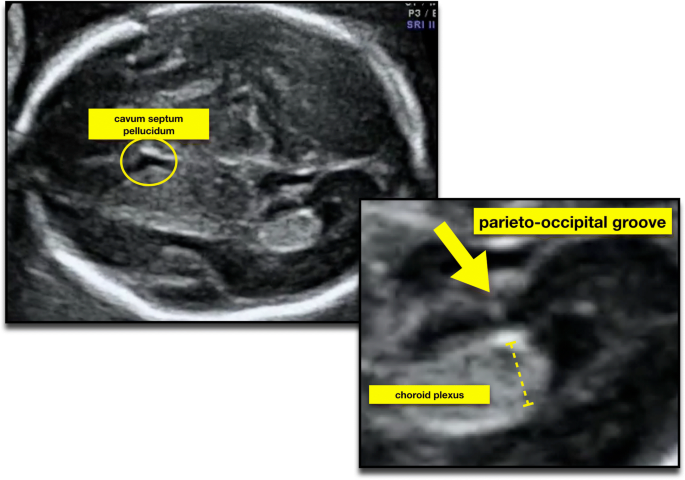
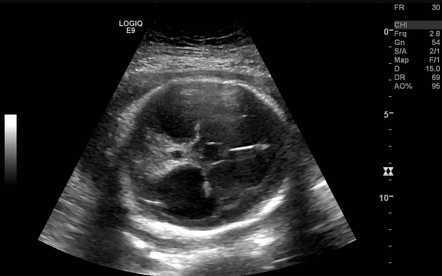
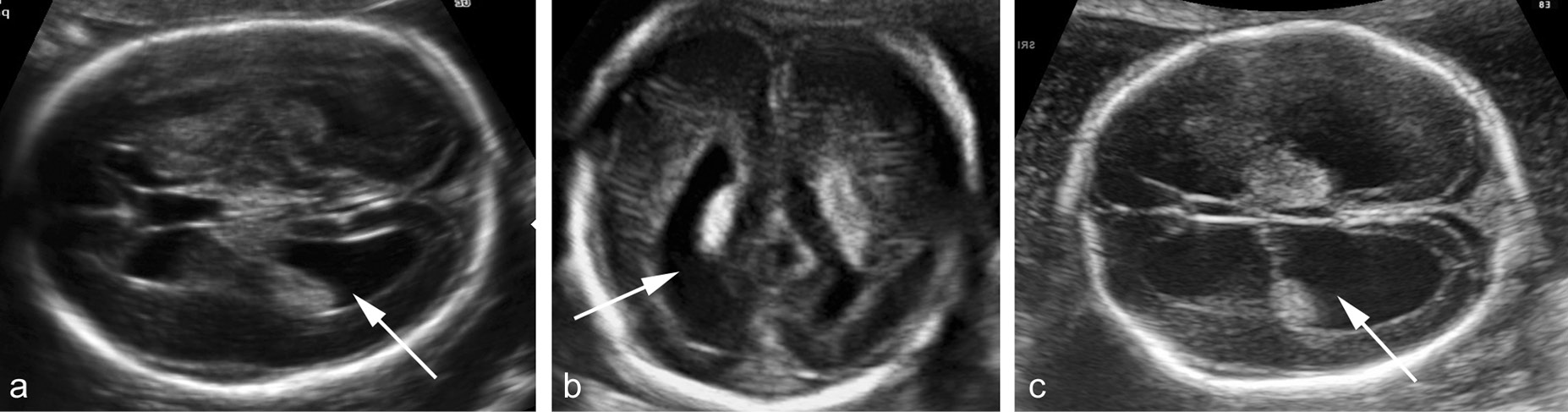
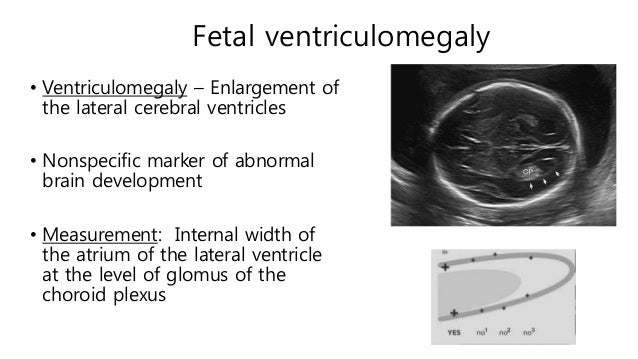
Bilateral Ventriculomegaly Prognosis
Iame is accredited by the accreditation council for continuing medical education.
Bilateral ventriculomegaly prognosis. However it has been found to occur before birth in either the earlier or later stages. A normal variants b developmental cystic lesions c cysts due to perinatal injury d vascular cystlike structures e hemorrhagic cysts and f infectious cysts. The differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions at head ultrasonography us includes a broad spectrum of conditions. These lesions vary in prevalence from common cavum of the septum pellucidum subependymal cyst.
In a minority of cases minor lateral ventriculomegaly 6 20 of cases and corpus callosal dysgenesis 6 10 of cases is also present 5 9. Polymicrogyria pmg is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex this abnormality can affect either one region of the brain or multiple regions. Not many large studies have reported the true impact of lower grade intraventricular hemorrhages in preterm infants. Epidemiology they are thought to be present in 4 5 of karyotypically normal fetuses.
B coronal t2 weighted mr image shows cerebellar hypoplasia multiple bilateral subcortical cysts in the cerebellar hemispheres arrow cerebellar dysplasia generalized polymicrogyria arrowheads abnormal signal intensity of the supratentorial white matter absence of the septum pellucidum and marked ventriculomegaly. Ventriculomegaly associated with abnormalities and structural malformations of the fetus often has an unfavorable prognosis which varies from disability often mild to loss of the baby. Since 1992 the institute for advanced medical education has been a leading provider of continuing medical education providing practice changing experiences for physicians nurses technologists and other health care professionals. However in cases of mild isolated ventriculomegaly there is a 90 chance of a normal outcome.
Any patient who develops neurologic deterioration weeks to months following tbi should be evaluated for the possibility of normal pressure hydrocephalus. This ventriculomegaly is often secondary to diffuse brain atrophy and radiographic features rarely help make the distinction between atrophy and normal pressure hydrocephalus. A regional cohort study of infants born at 23 to 28 weeks gestation and admitted to a nicu between 1998 and 2004. Echogenic intracardiac focus eif is a relatively common sonographic observation that may be present on an antenatal ultrasound scan.
They may be more commo.