Bilateral Vestibulopathy Causes
Common vestibular disorders benign paroxysmal positional vertigo bppv.
Bilateral vestibulopathy causes. The immediate reaction by a competent physician is to first rule out life threatening causes heart disease cerebrovascular disease seizure disorder meningitis brain tumor etc. 1 as a result of a reduced gain of the avor the visual world cannot be stabilized on the retina during high acceleration head movements which leads to head movement induced oscillopsia 9 and reduced dynamic visual acuity 49. It happens when tiny. Tests for syphilis an antibody test for autoimmune inner ear disease or audiograms may also be important.
Bilateral vestibulopathy bvp is damage to the vestibular system in the inner ear which is part of the balance system. Bvp is a common cause of balance problems and falls especially in older people. Hearing seems to be more sensitive to the disease process of meniere s than does vestibular function. Unlike in unilateral loss of vestibular function where compensation is typical many patients with bilateral vestibulopathy experience chronic oscillopsia due to failure of the vestibulo ocular reflex and gait instability due to failure of vestibulo spinal reflexes.
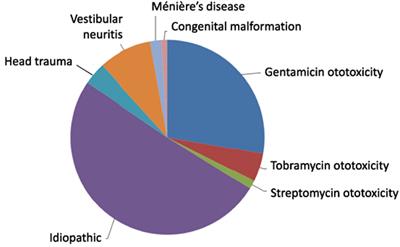
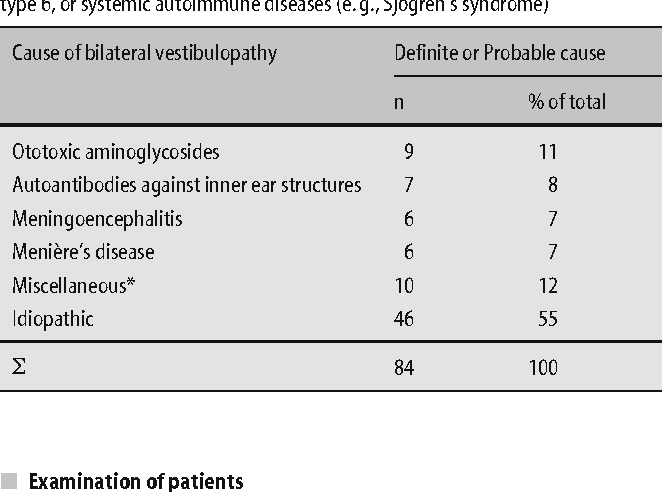
Single known cause of bilateral vestibulopathy accounting for 15 50 of all other antibiotic ototoxins are streptomycin tobramycinand vancomycin. However 10 of vestibulopathy is also caused due to infection bilateral ear surgery sarcoidosis meniere s disease congenital disorder migraine and mondini malformation etc. Rare causes of bilateral vestibulopathy. Pathophysiology bilateral impairment or loss of peripheral vestibular input causes deficits of vestibulo ocular and vestibulo spinal reflexes orientation navigation and spatial memory.
Bilateral menière s disease autoimmune diseases meningitis and bilateral vestibular schwannoma as well as an association with cerebellar degeneration cerebellar ataxia neuropathy vestibular areflexia syndrome canvas. Meniere s disease while associated with repeated attacks of vertigo rarely causes bilateral vestibular loss. Bilateral means the damage is on both sides. There are several different causes of bilateral vestibulopathy including gentamicin toxicity but the rotary chair test will determine the effects on both ears.
This is the most common cause of positional vertigo a sudden feeling that you re spinning or swaying. In general in the long term there is no improvement of vestibular function. Apart from this age is also a major risk factor for this disease.