Neurosensory Hearing Loss Pediatric

Bor syndrome is autosomal dominant and consists of hearing loss auricular malformations branchial arch closure defects preauricular pits and tags and renal anomalies.
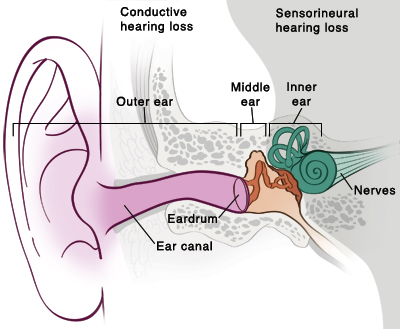
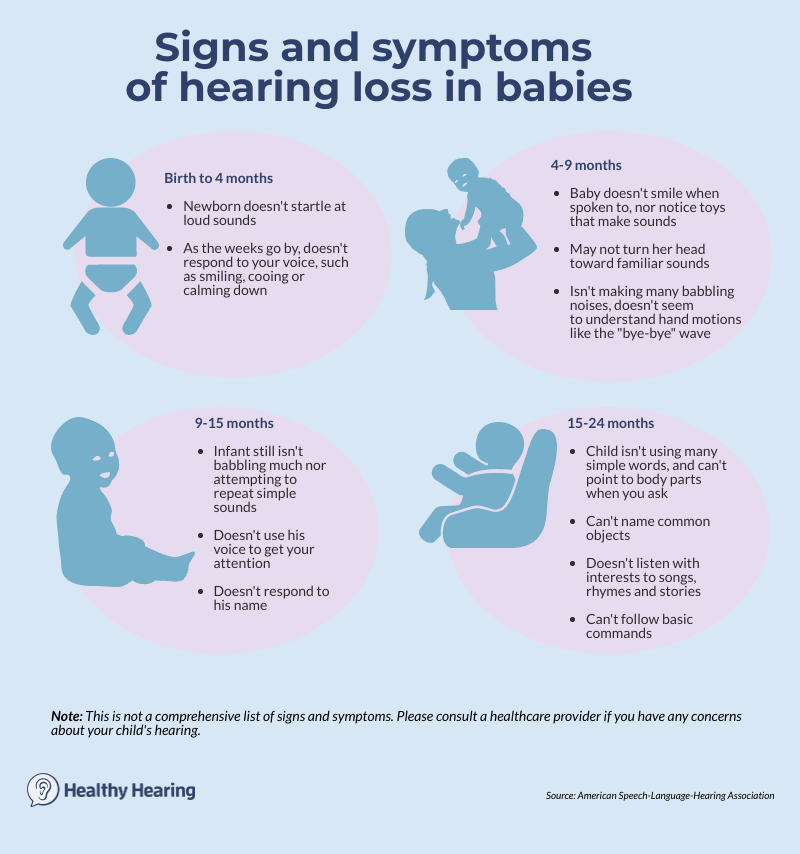
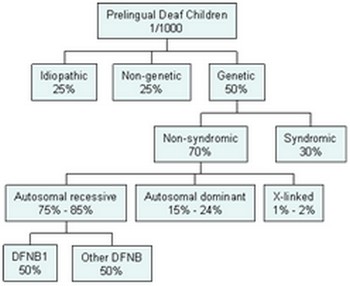
Neurosensory hearing loss pediatric. Sensorineural hearing loss can be present at birth. In march this year i decided to go ahead with a hearing test at the neurosensory chermside clinic i remember the clinician mitchell asking me what you brings you here today. Sensorineural hearing loss is primarily a disease of the auditory portion of the inner ear the cochlea. 1 although these numbers indicate that snhl is relatively common it remains underappreciated and underdiagnosed in children.
Neurosensory hearing losses are caused by damage to the nerves involved with hearing. Hair cells can not regenerate. Sensorineural hearing loss arises from damage to either the cochlea in the inner ear or the auditory nerve. Since having my two children i really wanted to hear them when they spoke to me in the park and i felt i was missing out on conversations with them in restaurants.
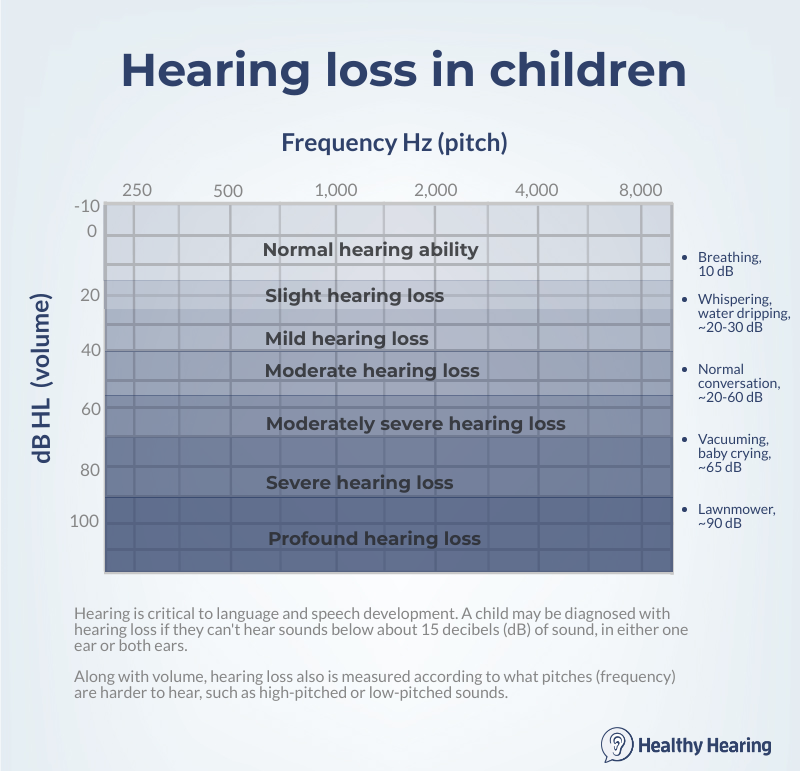
Some examples would be hearing loss caused by old age noise exposure severe infection of the ear acoustic trauma such as an explosion going off nearby or damage caused by medications. It is a permanent condition that usually affects both ears. They convert the mechanical sound waves into neural information for transmission to the brain. The incidence of severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss snhl in children is approximately 1 2000 at birth and 6 1000 by 18 years of age.
Or it can occur later in life. It normally affects both ears. Patients with bor syndrome may also demonstrate lacrimal duct stenosis a narrow face palatal abnormalities and anomalies of the bladder and ureters. Trouble following group conversations muffled conversation sounds inability to hear well when there s a lot of background noise difficulty hearing high pitched sounds dizziness balance problems tinnitus which occurs when you hear ringing or buzzing sounds in your ear.
All of these cause damage to the nerve endings or the nerve in the ear. Sensorineural hearing loss involves problems with the transmission of sound information from hair cells deep within the ear to the nerve that sends sound information to the brain. For example the severe to profound unilateral losses are often not recognized until kindergarten when the child undergoes the first audiometric evaluation. Once you develop sensorineural hearing loss you have it for the rest of your life.