Posterior Uveitis Ultrasound

Hence it is also known as choroiditis.
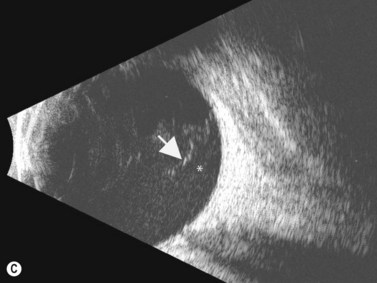
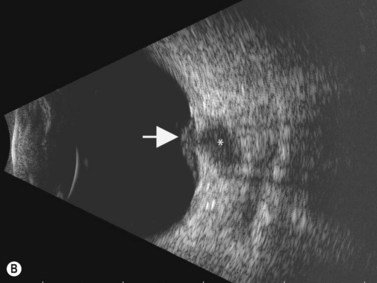
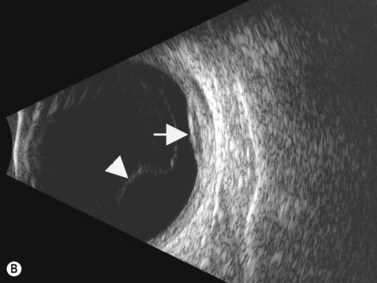
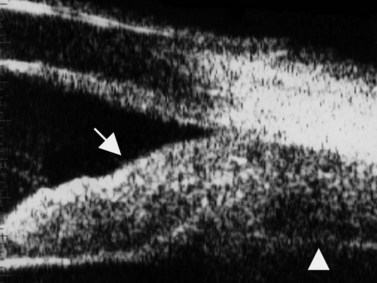
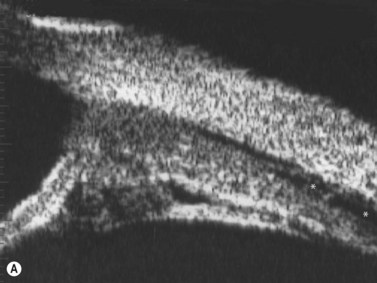
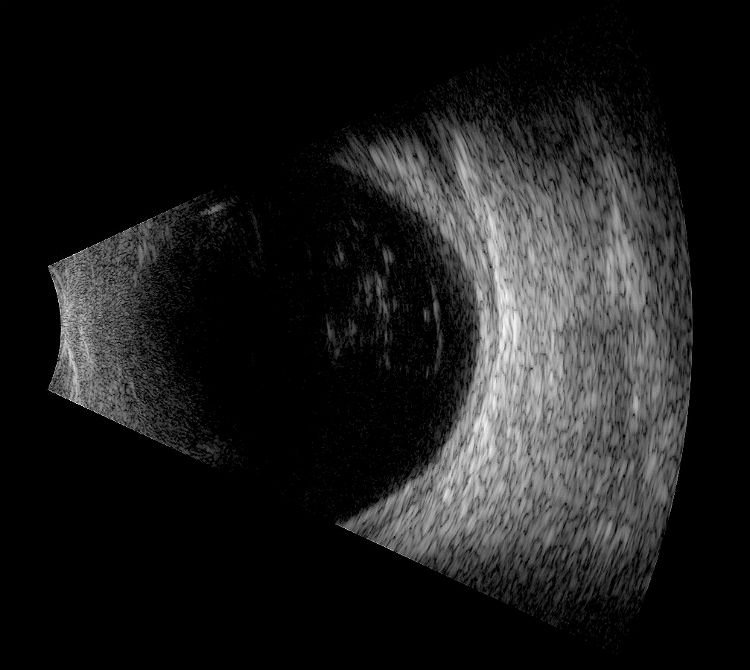
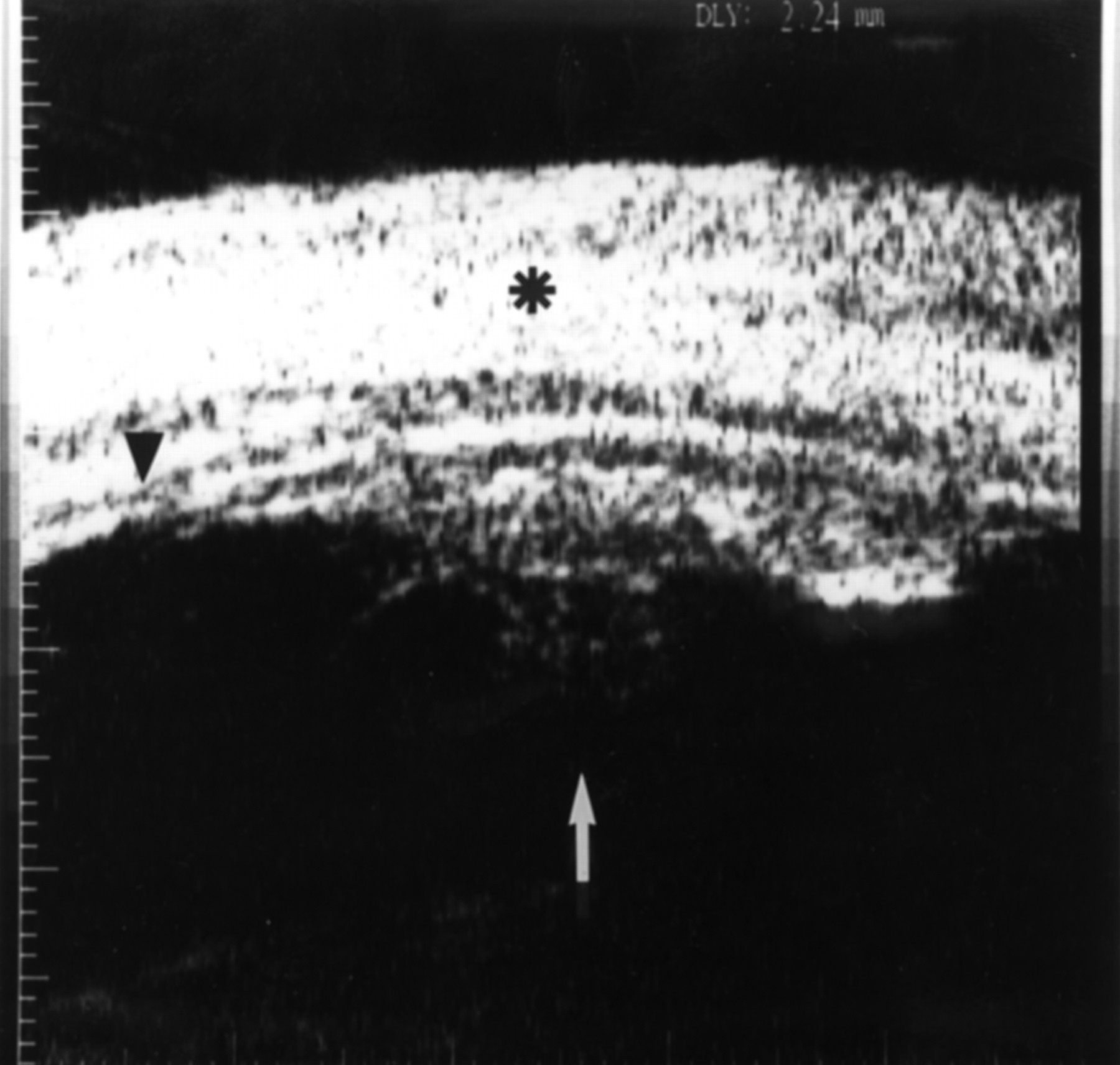
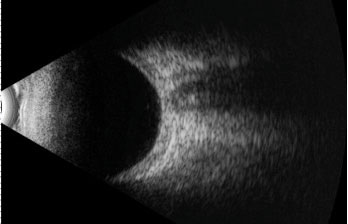
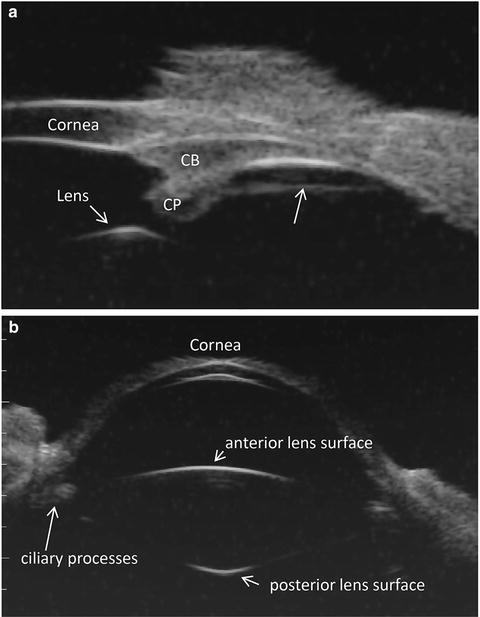
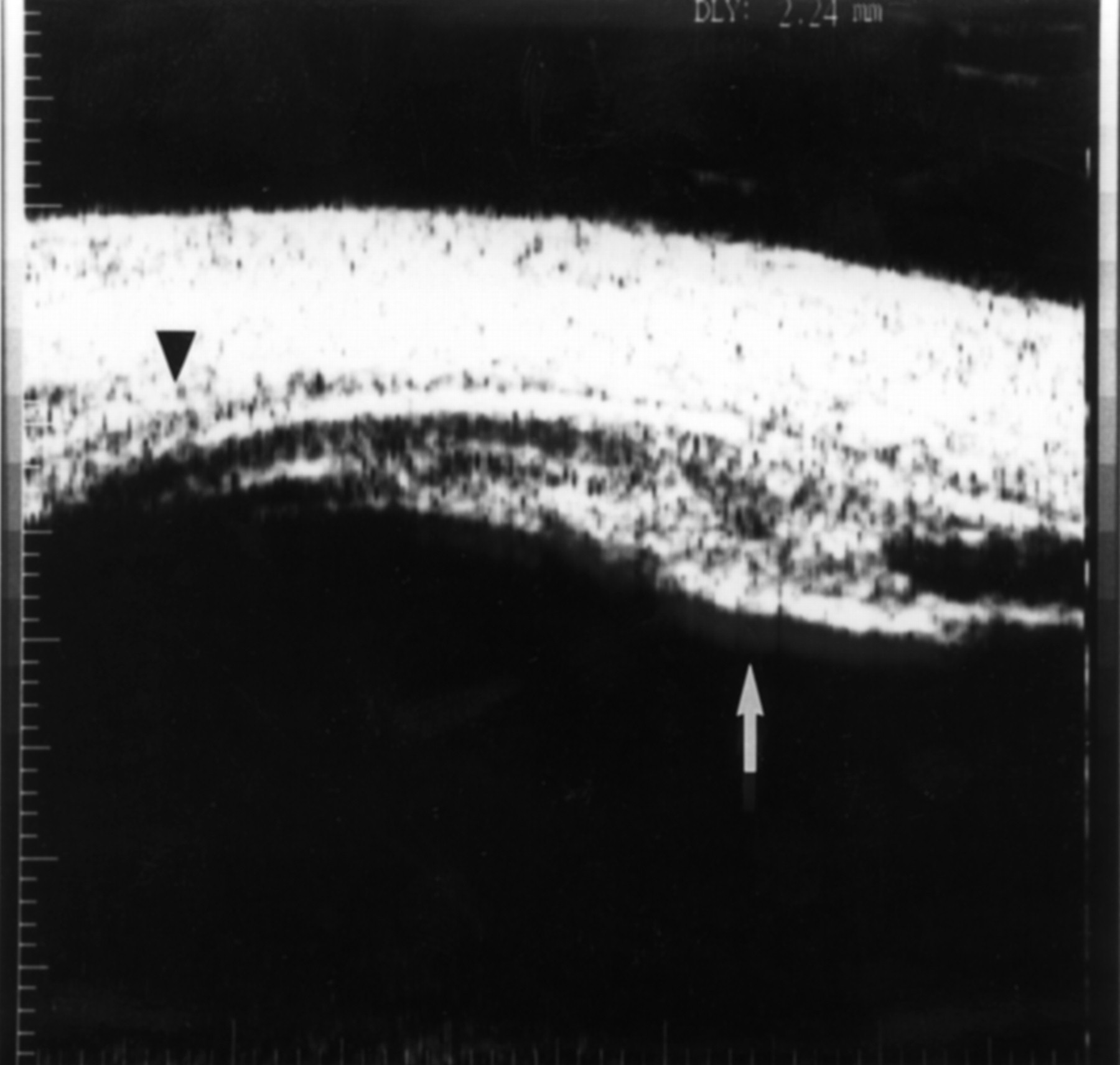
Posterior uveitis ultrasound. Ultrasound can provide excellent pictures of anterior uvea vitreous base and peripheral retina in normal eyes and also in eyes with intermediate uveitis 1 3. Posterior uveitis may affect the retina and or the optic nerve and may lead to permanent loss of vision. In that perspective ultrasound biomicroscopy ubm promises to be a valuable additional diagnostic tool. B mode ultrasound in the uveitis in the psoriatic arthritis without skin lesion in our rheumatological clinical practice several cases of inflammatory arthropathy associated with uveitis evaluate future studies will better signal the intensity of these findings of vitreous humor alterations and.
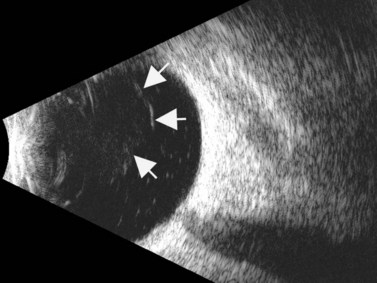
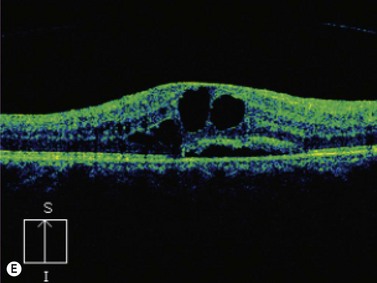
Background clinical examination of the region of the eye mainly affected in patients with intermediate uveitis is difficult and often hampered by media opacities. On ultrasound rd appears as a hyperechoic rippled or undulating line membrane in the posterior to lateral globe. Posterior uveitis also known as choroiditis refers to inflammation of the choroid the back part of the uvea. Anatomy physiology the uvea is a highly vascular layer that lines the sclera and its principal function is to provide nutrition to the eye.
Contact your doctor if you think you have the warning signs of uveitis. Posterior uveitis is the rare form of the disorder and is the type of uveitis most associated with loss of vision. In general ultrasonography is considered superior to ct in imaging for posterior scleritis but the latter can be helpful in ruling out idiopathic orbital inflammation and myositis. Panuveitis also known as diffuse uveitis is the inflammation of all uveal components of the eye with no particular site of predominant inflammation.
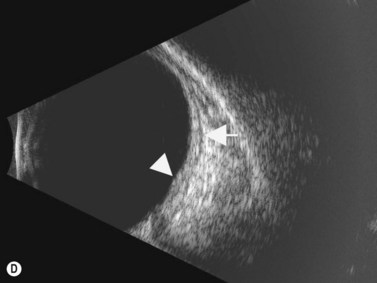
When to seek medical advice. The 20 mhz frequency probes can detect the typical snowbank in intermediate uveitis 50 ultrasonography is also useful in the detection of posterior vitreous detachment a common finding in eyes with vitreous inflammation 51 ultrasound can be used to monitor serous retinal detachments in vkh disease and sympathetic ophthalmia. Posterior uveitis is a condition involving inflammation of the choroid. Posterior uveitis affects a layer on the inside of the back of your eye either the retina or the choroid.
Ct can help identify posterior inflammation demonstrating increased choroidal thickness. However currently oct is a preferred modality for monitoring serous detachment. The choroid is one of 3 parts that make up the uvea and it is located in the back part of it posterior uveitis can be caused by both infectious and non infectious factors and any individual may be affected.