Bilateral Upper Limb Thoracic Outlet Syndrome

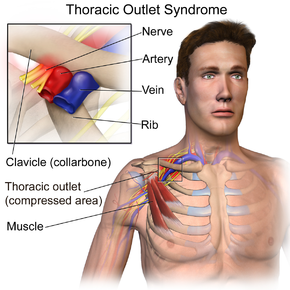
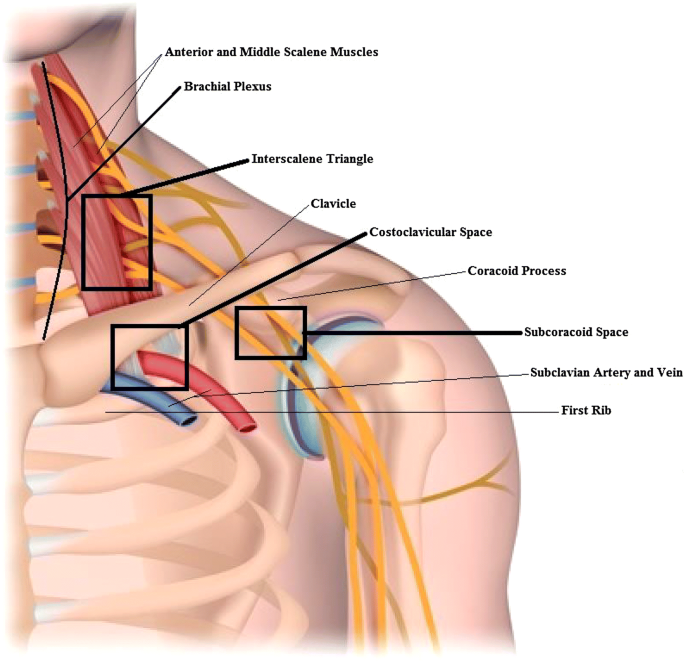
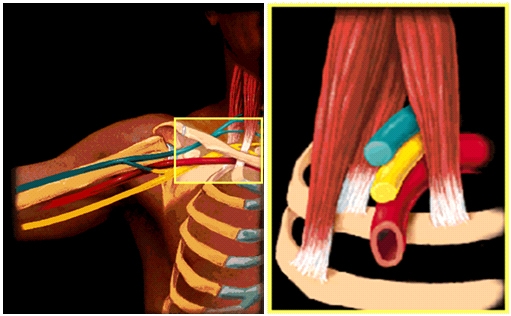
Thoracic outlet syndrome tos is a term used to describe a group of disorders that occur when there is compression injury or irritation of the nerves and or blood vessels arteries and veins in the lower neck and upper chest area.
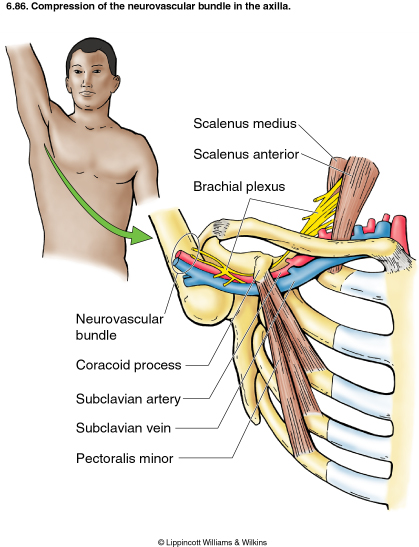
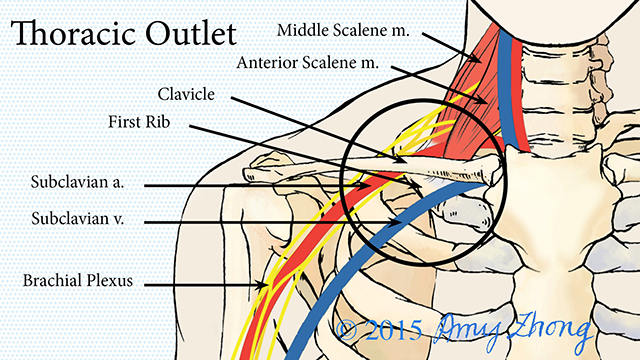
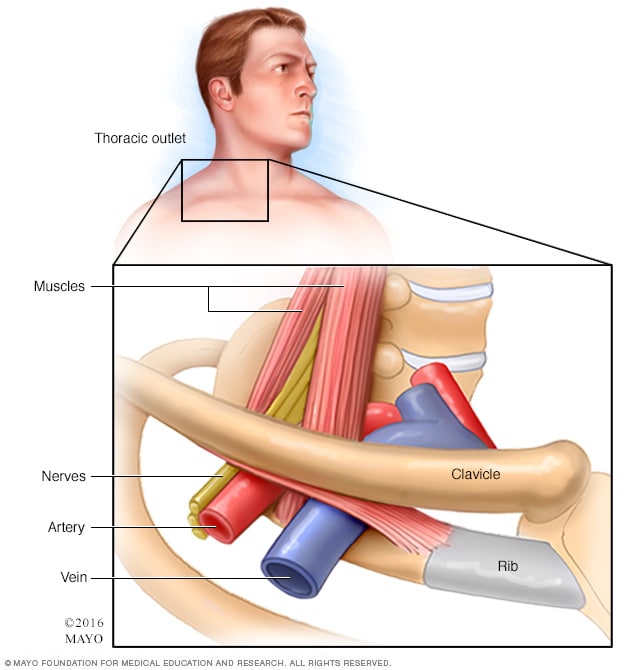
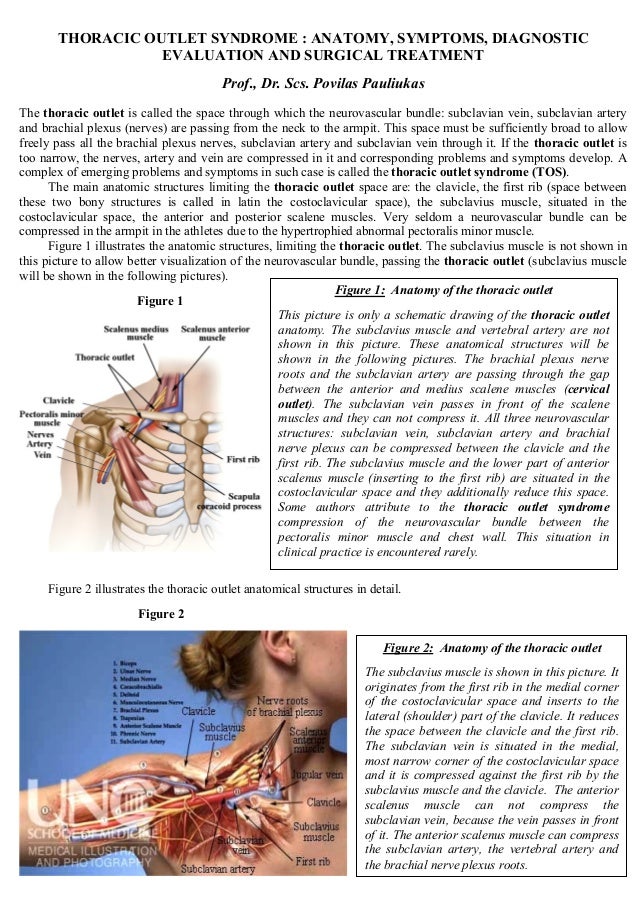
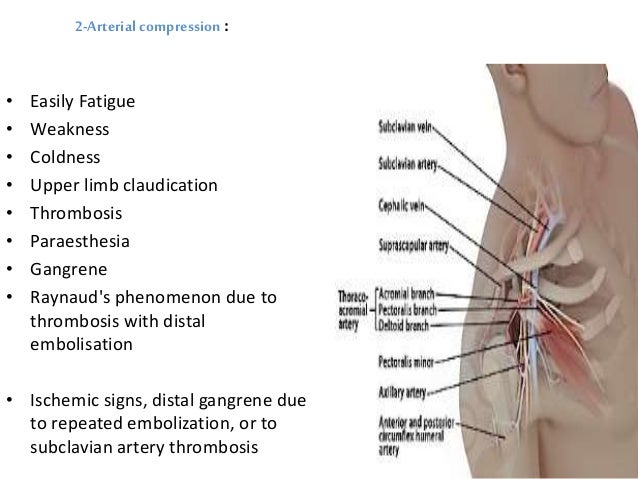
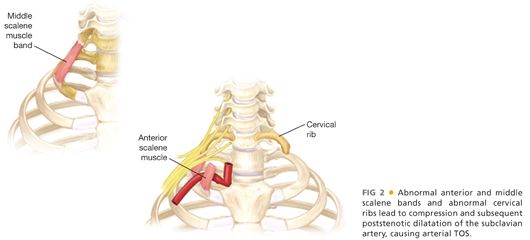
Bilateral upper limb thoracic outlet syndrome. Vascular thoracic outlet syndrome. The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that come from your spinal cord and control muscle movements and sensation in your shoulder arm and hand. This most common type of thoracic outlet syndrome is characterized by compression of the brachial plexus. Neurogenic neurological thoracic outlet syndrome.
The clinical presentation typically reflects the component of the neurovascular bundle affected. Thoracic outlet syndrome is named for the space the thoracic outlet between your lower neck and upper chest where this grouping of nerves and blood vessels is found. Surgery for neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome ntos decompression has a failure rate of 25 to 30 primarily due to postoperative scar tissue com pressing the brachial plexus bp 1 whereas scarring can be prevented by wrapping the bp with physical bar riers successful wrapping materials have not been found to date. Patients with thoracic outlet syndrome will most likely present pain anywhere between the neck face and occipital region or into the chest shoulder and upper extremity and paresthesia in upper extremity.